Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Jaffe, A. L.*; Thomas, A. D.*; He, C.*; Keren, R.*; Valentin-Alvarado, L. E.*; Munk, P.*; Bouma-Gregson, K.*; Farag, I. F.*; 天野 由記; Sachdeva, R.*; et al.
mBio, 12(4), p.e00521-21_1 - e00521-21_21, 2021/08
被引用回数:22 パーセンタイル:90.08(Microbiology)Candidate Phyla Radiation (CPR) bacteria are small, likely episymbiotic organisms found across Earth's ecosystems. Despite their prevalence, the distribution of CPR lineages across habitats and the genomic signatures of transitions amongst these habitats remain unclear. Hear, we expand the genome inventory for Absconditabacteria (SR1), Gracilibacteria, and Saccharibacteria (TM7), CPR bacteria known to occur in both animal-associated and environmental microbiomes, and investigate variation in gene content with habitat of origin. By overlaying phylogeny with habitat information, we show that bacteria from these three lineages have undergone multiple transitions from environmental habitats into animal microbiomes. Based on co-occurrence analyses of hundreds of metagenomes, we extend the prior suggestion that certain TM7 have broad bacterial host ranges and constrain possible host relationships for SR1 and Gracilibacteria. Full-proteome analyses show that animal-associated TM7 have smaller gene repertoires than their environmental counterparts and are enriched in numerous protein families, including those likely functioning in amino acid metabolism, phage defense, and detoxification of peroxide. In contrast, some freshwater TM7 encodea putative rhodopsin. For protein families exhibiting the clearest patterns of differential habitat distribution, we compared protein and species phylogenies to estimate the incidence of lateral gene transfer and genomic loss occurring over the species tree. These analyses suggest that habitat transitions were likely not accompanied by large transfer or loss events, but rather were associated with continuous proteome remodeling. Thus, we speculate that CPR habitat transitions were driven largely by availability of suitable host taxa, and were reinforced by acquisition and loss of some capacities.
 and metal transformations associated with novel bacteria and archaea in deep terrestrial subsurface sediments
and metal transformations associated with novel bacteria and archaea in deep terrestrial subsurface sedimentsHernsdorf, A. W.*; 天野 由記; 宮川 和也; 伊勢 孝太郎; 鈴木 庸平*; Anantharaman, K.*; Probst, A. J.*; Burstein, D.*; Thomas, B. C.*; Banfield, J. F.*
ISME Journal, 11, p.1915 - 1929, 2017/03
被引用回数:90 パーセンタイル:96.01(Ecology)地層処分システムにおける微生物影響の可能性を評価するために、北海道の幌延深地層研究センター地下施設を利用して、堆積岩地下の生態系における微生物群集構造と代謝機能について調査を行った。全体として、微生物生態系は多様な系統群からなる微生物種で構成されており、その多くはこれまで培養されていない生物門に属していることが示された。大部分の微生物種は、酸化型[NiFe]ヒドロゲナーゼあるいはフェレドキシンをベースとする代謝経路を可能にする電子分岐型[FeFe]ヒドロゲナーゼを介して水素代謝をおこなうことが明らかになった。水素代謝と関連して、多くの微生物が炭素,窒素,鉄および硫黄を代謝することが推定された。特に、ANME-2dというメタン酸化を行う古細菌として知られている未培養微生物が、鉄関連の代謝反応を行う可能性が示唆された。得られた結果から、幌延堆積岩環境における微生物群集の生態学的概念モデルを推定した。
増渕 隆*; 渡口 和樹*; 林 秀謙*; 池永 裕*; 佐藤 勝也; 大野 豊
JAEA-Review 2015-022, JAEA Takasaki Annual Report 2014, P. 106, 2016/02
We conducted the gene function analysis of the high ethyl caproate producing sake yeast mutant (No.227) generated by ion beam breeding in order to develop a new method for sake yeast screening and find factors contributing the reduced ability to alcohol fermentation. The genome sequences of the No.227 and Kyokai 901 (its parental strain) were determined by a whole-genome shotgun strategy using pyrosequencing method. And the determined sequences were compared with that of the sake yeast strain Kyokai 7, which is characterized by the fermentation properties. Consequently, the No.227 carried mutations in the 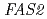 and
and 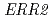 genes as heterozygous state. It was suggested that these mutations in the
genes as heterozygous state. It was suggested that these mutations in the 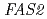 and
and 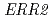 genes in the No.227 might be attributed to the high ethyl caproate production and the low alcohol fermentation ability, respectively.
genes in the No.227 might be attributed to the high ethyl caproate production and the low alcohol fermentation ability, respectively.
鳴海 一成; 菊地 正博; 舟山 知夫; 佐藤 勝也
放射線生物研究, 34(4), p.401 - 418, 1999/00
生物は常にDNA損傷を被る環境に曝されており、生命の維持はDNA損傷をどれだけ効率よく正確に修復できるかに懸かっている。したがって、生物のDNA修復能力の限界を見極めることは、巧妙な生命現象へのわれわれのより深い理解にとって大切なことであるのみならず、生命維持機能を増強する方法の開発に方向性を与えることにも繋がる。今までともすれば奇異な目で見られることもあった放射線抵抗性細菌デイノコッカス・ラジオデュランスを、ほかの生物と同様に放射線生物研究の対象として扱い、ほかの生物とどこが同じでどこが違うのかを明らかにして、その極めて高いDNA修復能力を分子レベルで解明する研究が、最近になって急速に進展しつつある。本稿では、デイノコッカス・ラジオデュランスの特徴的側面、及びわれわれの研究室で得られた最新のデータをまじえ、DNA修復遺伝子群の解析に関する最近の進展状況について述べる。
佐藤 勝也; 武田 喜代子*; 鳴海 一成*; 大津 直子*; 横山 正*
no journal, ,
根粒菌はマメ科植物と共生し、窒素栄養をマメ科植物に供給する。現在、化学肥料からの脱却を目指し、東南アジア等では、この共生関係を生かした根粒菌バイオ肥料の利用が奨励されている。しかし、化学肥料とは異なり、バイオ肥料は、輸送や保存時の高温による接種菌の活性低下等の問題があり改良が望まれている。これまで我々は、ダイズ根粒菌の温帯優良接種菌株である USDA110株を対象としたイオンビーム突然変異育種を行ってきた。そして、42
USDA110株を対象としたイオンビーム突然変異育種を行ってきた。そして、42 Cの液体培地中で少なくとも1週間は高い生存率を維持することが可能な高温耐性変異株の取得に成功した。本研究では、次世代シークエンサーを用いて高温耐性変異株の全ゲノムを解読し、野生株との塩基配列の比較によってDNA変異部位を同定した。ゲノムDNA塩基配列の比較解析の結果、高温耐性変異株M14において、1.27Mbpの逆位という大規模なゲノム構造変異、及び一塩基置換・欠失及び挿入などの18ヶ所の小規模なDNA塩基変異が存在することを明らかにした。これらの大規模な構造変異あるいは小規模な遺伝子変異がM14株の高温耐性に関与している可能性が考えられた。
Cの液体培地中で少なくとも1週間は高い生存率を維持することが可能な高温耐性変異株の取得に成功した。本研究では、次世代シークエンサーを用いて高温耐性変異株の全ゲノムを解読し、野生株との塩基配列の比較によってDNA変異部位を同定した。ゲノムDNA塩基配列の比較解析の結果、高温耐性変異株M14において、1.27Mbpの逆位という大規模なゲノム構造変異、及び一塩基置換・欠失及び挿入などの18ヶ所の小規模なDNA塩基変異が存在することを明らかにした。これらの大規模な構造変異あるいは小規模な遺伝子変異がM14株の高温耐性に関与している可能性が考えられた。
増淵 隆*; 日向 弘和*; 池永 裕*; 林 秀謙*; 佐藤 勝也; 大野 豊
no journal, ,
群馬県では、オリジナルの吟醸用清酒酵母を開発するために、 C
C (220MeV)のイオンビーム照射による突然変異で新たな吟醸用清酒酵母の開発を行っており、これまでに吟醸酒特有の香気成分であるカプロン酸エチルを高生産する優良清酒酵母(No.227)を選抜した。しかし、カプロン酸エチル高生産酵母は発酵能が弱くなることがあり、また、変異株の選抜・機能評価は多大な手数と時間を必要とし、研究の遂行を困難にする一因となっている。本研究はイオンビーム変異により得られた酵母の全ゲノムDNA塩基配列を解読し、発酵特性等の機能とゲノム情報が既に明らかとなっている酵母と比較することで、酵母選抜のメルクマールとなる香気生成能・発酵能に関与する遺伝子群を特定すること目的として行った。
(220MeV)のイオンビーム照射による突然変異で新たな吟醸用清酒酵母の開発を行っており、これまでに吟醸酒特有の香気成分であるカプロン酸エチルを高生産する優良清酒酵母(No.227)を選抜した。しかし、カプロン酸エチル高生産酵母は発酵能が弱くなることがあり、また、変異株の選抜・機能評価は多大な手数と時間を必要とし、研究の遂行を困難にする一因となっている。本研究はイオンビーム変異により得られた酵母の全ゲノムDNA塩基配列を解読し、発酵特性等の機能とゲノム情報が既に明らかとなっている酵母と比較することで、酵母選抜のメルクマールとなる香気生成能・発酵能に関与する遺伝子群を特定すること目的として行った。
天野 由記; Diamond, S.*; Lavy, A.*; Anantharaman, K.*; 宮川 和也; 岩月 輝希; 別部 光里*; 鈴木 庸平*; Thomas, B. C.*; Banfield, J. F.*
no journal, ,
We investigated the microbiology two Japanese subsurface research sites and compared the major groups of organisms lacking cultivated representatives found from other subsurface sites, including a Colorado aquifer and deep aquifers underlying the Crystal Geyser. We analyzed metagenomic data 19 samples from the Horonobe site and 7 from the Mizunami site. DNA sequences from each sample were assembled independently and scaffolds encoding the ribosomal protein S3 sequence were identified. The major characteristic of the microbiology of the Mizumani site that distinguished it from the Horonobe site is local very high abundances of Nitrospirae, Parcubacteria, Ignavibacteria, ANME-2D and Micrarchaeota. In contrast, the Horonobe site has locations that are highly enriched in Altarchiales, Syntrophobacteriales, Atribacteria, ANME-2D and Methanogens. Beyond reshaping the Tree of Life, the societal importance of these discoveries remains little known. However, given the huge inventory of new groups of proteins and pathways in the genomes of these organisms, it is reasonable to anticipate major discoveries will hold relevance, for example, in terms of pharmaceutical discovery. Given the importance of the subsurface as a potential host environment for storage of nuclear waste, finding some commonality would indicate the general relevance of information from one site for prediction of the characteristics of other sites.